Application of thin plate parts
Thin-plate parts are common engineering products, and are widely used in automobiles, aerospace, household appliances, and metal fixtures.
During the processing of thin-walled parts, the problem of deformation often occurs. What should be done at this time? Let me explain an example with my own case analysis

Anyone who has worked on aluminum parts knows that there is a big difference in the processing of 6 series (mainly magnesium and silicon) and 7 series (mainly zinc). If the content is too large, I will not explain it in detail here. As an example, you may understand. The Apple 6 and 6P shells are made of 6-series aluminum, and the result is a "curved door" event. Later, the 6S and 6P were replaced with 7 series aluminum. Here we can see that the 6 series is more plastic than the 7 series aluminum, which is easier to bend. Therefore, the common thin plate parts generally use 7 series aluminum.
1. Structural characteristics of parts
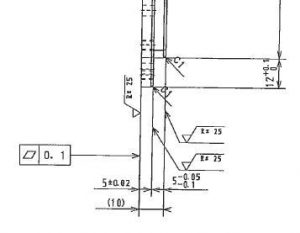
The size of this part is 310 * 310 * 10, the material is A7075, the quantity is 9 pieces, the thickness is 10mm, and the thinnest place is 5mm at the step. Here is also a through hole with a diameter of 206 in the middle with a tolerance of ± 0.02, ignoring the middle fine hole The rough hole position slot, here I only talk about the key point, this part processing is full CNC rough finishing, and the side hole is still the upper CNC (more on this later)
2. Problems and difficulties in processing
When processing this thin plate part, considering its thin wall and easy deformation, the process is divided into rough and fine processing. After finishing machining, when the part is in the compressed state on the worktable, use a dial indicator to test whether the deformation around the part meets the requirements of the drawing. Remove and then check. The 5 ± 0.02 size is out of tolerance, which affects the final assembly requirements.
Taking into account the accuracy of this large board part, the raw material we bought is a 12-thick board. The bottom surface is finally processed on the entire platen. 9 pieces are processed in sequence, and 3 of them are scrapped.Due to the difficulties caused by the deformation, there are huge uncertainties in the processing, and ultimately the size cannot be fully guaranteed.
This kind of typical thin parts, generally more than three or more, most of them use a surface grinder (large water grinder) to process the thickness, to minimize deformation and processing costs. Because the existing surface grinder equipment can not meet the processing of such large parts In the end, it can only be pinned to the CNC, plus the outbreak of the epidemic in the next year, except for the leadership of the entire department, I will be alone, and the result will not be able to be ground during finishing, which will deform the parts during the process and seriously affect the size and Geometric tolerance requirements.
3. Analysis and control of deformation reasons
The deformation of parts during processing includes:
(1) Deformation caused by redistribution of internal stress after machining of parts.
(2) The flatness of the positioning surface can not meet the requirements, and the deformation caused by the rebound.
(3) Deformation caused by improper clamping position, direction and stress point of parts.
(4) The machining allowance of the parts and the deformation caused by the cutting force during the machining process.
(5) Deformation caused by cutting heat during processing.
(6) Deformation caused by unreasonable part structure.
The parts deformation control methods are:
1. Eliminate stress and control deformation through heat treatment. Divided into roughing, semi-finishing and finishing processes, heat treatment is added to eliminate stress and stabilization treatment, so that parts can release machining stress and material stress, and improve the stability of dimensional accuracy of parts after finishing.
2. The deformation of the finished machining positioning surface is controlled. The reference surface is finished by grinding, grinding and other methods to improve the accuracy of the positioning surface to prevent springback deformation.
3. Improve the compression and clamping to control the deformation. Control the deformation by changing the clamping position, direction and force point, such as changing radial compression to axial compression.
4. Reduce cutting force to control deformation. In the finishing process, grinding, polishing and other processing methods with low cutting force can be used for processing, and methods of changing cutting parameters and reducing cutting consumption can also be used.
5. Reduce cutting heat control deformation. In order to prevent thermal deformation caused by cutting heat, cutting fluid can be used in processing, and the amount of cutting can be reduced.
6. Improve part structure or process method to control deformation. Reduce or control the deformation of the parts by improving the structure of the parts, such as adding support ribs, symmetrical shape design, etc .; improve the process and make the stress completely released.
After rough machining, the parts have undergone aging treatment, and the stress is released. Cutting fluid cooling is used in machining to prevent deformation caused by cutting heat. The roughing allowance is 1mm, and the cutting force and machining stress may also affect the deformation of the part. The clamping method is longitudinal (strength) clamping, and the clamping force is very large, which will cause great deformation. From the analysis, it is believed that the inappropriate clamping position, direction and stress point of the parts are the main reasons for the deformation.
(Note: The mechanical properties will change if the 7 series aluminum is artificially aged. If natural aging is done, the natural aging will take a long time and there is a risk of delivery delay)
Fourth, the technological measures taken for thin plate parts
1. Grinding positioning reference surface.
2. Make special tooling according to the shape of parts (flying surface on CNC machine tool)
3. The finishing allowance is reduced from 1mm to 0.5mm, the cutting is divided into three times during processing, and the last back-feeding amount is 0.05 ~ 0.1mm to control the deformation of parts caused by cutting force and processing stress during finishing
Note: The positioning of the special tooling cannot be higher than that of the parts; the tightening force of the screws should be uniform; the cutting parameters should be selected properly, and the tool should be kept sharp
To sum up
The application of thin-plate parts in modern products is very extensive. For the processing of thin-plate parts using traditional processing techniques and existing processing equipment, it is easy to cause parts to deform. Because the type and cause of deformation of thin-plate parts are analyzed first Furthermore, from the aspects of processing technology, processing technical conditions, processing tools, and clamping methods, the solution of processing deformation of thin plate parts is studied to achieve the purpose of reducing processing deformation.Most of them use grinding methods, and there are also some experienced teachers On the milling machine, the CNC adjusts the processing method according to the amount of deformation, but the general finish will be reduced and the dependence on the tool is strong.





